- Simple answer: T is the code for 12hr time in HHH:MM:SS. So, you'll get: $ export PS1+='T' 08:56:25 $ 08:56:26 $ 08:56:28 $ 08:56:30 $. In the case you have the PS1+ is appending onto an earlier configured PS1 variable - you'll need to modify to your needs.
- Time Machine is the backup mechanism of macOS, the desktop operating system developed by Apple.The software is designed to work with both local storage devices and network-attached disks, and is most commonly used with external disk drives connected using either USB or Thunderbolt.
- Mac Os Terminal Commands
- Mac Os Terminal Shortcut
- Mac Os Terminal Commands Pdf
- Mac Os X Terminal
- The Time Terminal Mac Os Catalina
The client terminal can be installed and run on computers with Mac OS using Wine. Wine is a free software that allows users of the Unix-based systems to run an application developed for the Microsoft Windows systems. Among all the Wine versions there is one for Mac OS.
Note that Wine is not a fully stable application. Thus, some functions in the applications you start under it may work improperly or not work at all. |
The easiest way to install the trading platform is download the ready-made package from the official website. Install the platform similarly to any other application – drag the platform icon to Applications and wait for the installation to complete.
The trading platform for Mac OS supports the Apple M1 chip and works reliably on any system version including Big Sur.
Terminal is the terminal emulator included in the macOS operating system by Apple. Terminal originated in NeXTSTEP and OPENSTEP, the predecessor operating systems of macOS. As a terminal emulator, the application provides text-based access to the operating system, in contrast to the mostly.
The installation package is compiled using CrossOver technology. This platform is based on Wine, but unlike other projects and Wine itself, CrossOver is a commercial product. Therefore, its development is much faster: the environment is optimized for better performance of Windows applications, while detected errors are quickly fixed. In contrast to 'pure' Wine, CrossOver has more specialized nature as it is aimed at supporting the most popular office and other Windows applications. Compatibility with these applications is extensively tested and debugged, so they tend to run more stable than in Wine. The trading platform is among these applications.
You do not need to have CrossOver on your computer to install the platform from the ready-made DMG package. Accordingly, its use is absolutely free. You do not need to download any additional components or make any complex adjustments. The platform is immediately ready to go after being installed from the package.
If this does not suit you for some reason, below is an alternative way to launch the platform on your Mac.
PlayOnMac Installation
PlayOnMac is a Wine-based software for easy installation of Windows applications on Mac OS.
To install PlayOnMac, open the product's official web site, move to Downloads section and click the link for downloading the latest version.
After downloading the DMG package, launch it from Downloads section of your system:
PlayOnMac first launch window will appear. After clicking 'Next', the installer will start checking and installing the various components necessary for work.
The first necessary component is XQuartz. This is a software for using X Window System on Mac OS. X Window System provides standard tools and protocols for building the graphical user interface in Unix-like OS.
If you have already installed XQuartz or want to install it later, select 'Don't install XQuartz for the moment' or 'I've downloaded file by myself', respectively.
XQuartz installation is performed in several stages. First of all, you should read the important information (Read Me) and accept the license conditions.
Before the installation, Mac OS security system will ask you to enter your account's password:
Wait for the installation to complete. For changes to take effect, you should restart your PC.
Mac Os Terminal Commands
After restarting the system, launch PlayOnMac again from the setup file in Downloads folder. The first launch window will appear again. This time, the installer will offer to install MS Windows fonts necessary for correct operation.
Accept the license agreement conditions and wait till the installation is complete. After that, PlayOnMac is ready for use. Its main window will appear:
Updating Wine
Wine is installed together with PlayOnMac.
Mac Os Terminal Shortcut
To upgrade Wine to the latest version, open PlayOnMac upper menu and select Manage Wine Versions:
The window with Wine versions available for installation will open. Select the latest version.
Move the latest Wine version to the right side of the window. The installation will start.
After the installation is complete, the new version of Wine will appear in the left part of PlayOnMac Wine versions manager window. You can then close the window and install the trading terminal.
Terminal Installation
To install the terminal, download the installer 'mt4setup.exe'. After the download is complete, launch the setup file. PlayOnMac will be used automatically to open it.
The standard terminal installation process with all its stages will start:
Mac Os Terminal Commands Pdf
When the installation is complete, PlayOnMac will offer you to create the shortcuts for the terminal components - the client terminal itself and MetaEditor:
Mac Os X Terminal
After creating the necessary shortcuts, you can start using the client terminal. Double click on it in PlayOnMac window to launch the terminal.
Terminal Data Directory
PlayOnMac creates a separate virtual logical drive with necessary environment for each installed program. The default path of the installed terminal's data folder is as follows:
LibraryPlayOnMacWinePrefixClient_Terminal_DriveCProgramFilesClient Terminal |
The Time Terminal Mac Os Catalina
| Developer(s) | Apple Inc. |
|---|---|
| Operating system | macOS |
| Platform | ARM64, x86-64, IA-32, PowerPC |
| Type | Terminal emulator |
| Website | www.apple.com/macosx/features/unix/ |
Terminal (Terminal.app) is the terminal emulator included in the macOSoperating system by Apple.[1] Terminal originated in NeXTSTEP and OPENSTEP, the predecessor operating systems of macOS.[2]
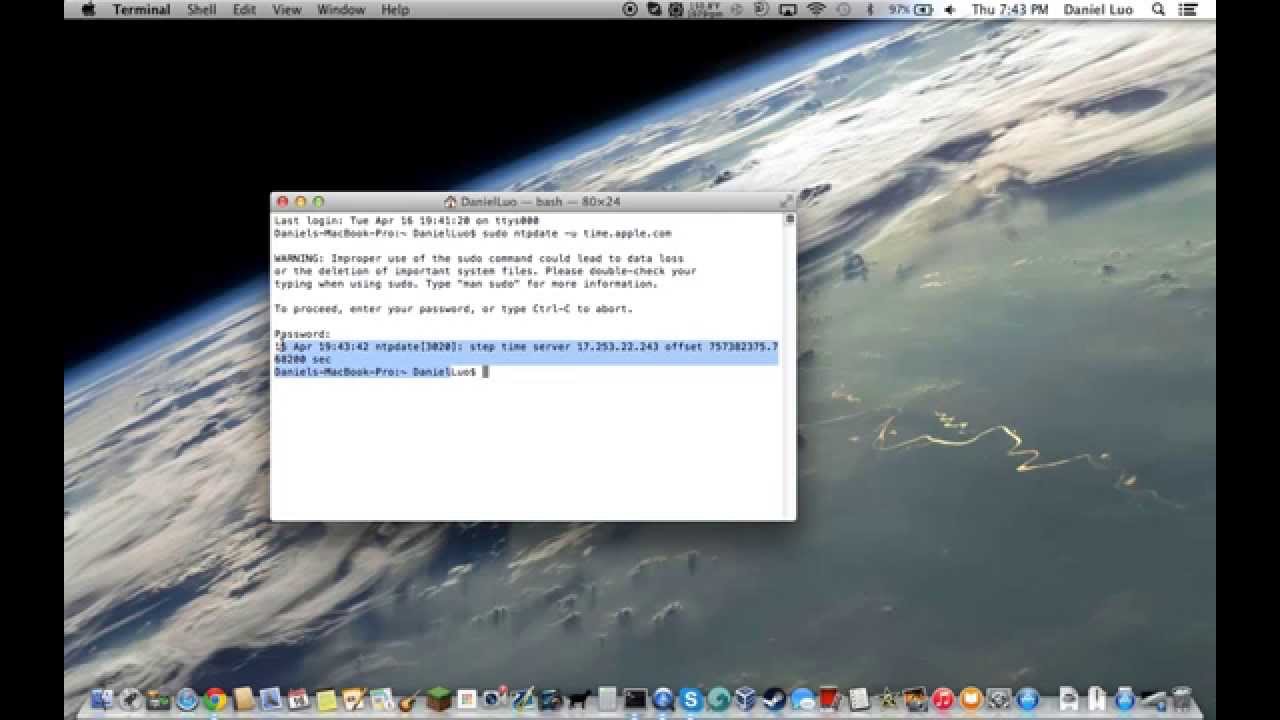
As a terminal emulator, the application provides text-based access to the operating system, in contrast to the mostly graphical nature of the user experience of macOS, by providing a command-line interface to the operating system when used in conjunction with a Unix shell, such as zsh (the default shell in macOS Catalina[3]).[4] The user can choose other shells available with macOS, such as the KornShell, tcsh, and bash.[4][5]
The preferences dialog for Terminal.app in OS X 10.8 (Mountain Lion) and later offers choices for values of the TERM environment variable. Available options are ansi, dtterm, nsterm, rxvt, vt52, vt100, vt102, xterm, xterm-16color and xterm-256color, which differ from the OS X 10.5 (Leopard) choices by dropping the xterm-color and adding xterm-16color and xterm-256color. These settings do not alter the operation of Terminal, and the xterm settings do not match the behavior of xterm.[6]
Terminal includes several features that specifically access macOS APIs and features. These include the ability to use the standard macOS Help search function to find manual pages and integration with Spotlight.[citation needed] Terminal was used by Apple as a showcase for macOS graphics APIs in early advertising of Mac OS X,[citation needed] offering a range of custom font and coloring options, including transparent backgrounds.
See also[edit]
- iTerm2, GPL-licensed terminal emulator for macOS
- Terminator, open-source terminal emulator programmed in Java
References[edit]
- ^'What Is Mac OS X - All Applications and Utilities - Terminal'. Apple Inc. Archived from the original on May 10, 2013.
- ^Wünschiers, Röbbe (January 1, 2004). Computational Biology: Unix/Linux, data processing and programming : with 19 figures and 12 tables. Springer Science & Business Media. ISBN9783540211426.
- ^'Use zsh as the default shell on your Mac'. Apple Support. Retrieved January 18, 2020.
- ^ abMcElhearn, Kirk (December 26, 2006). The Mac OS X Command Line: Unix Under the Hood. John Wiley & Sons. ISBN9780470113851.
- ^Kissell, Joe (January 1, 2009). Take Control of the Mac Command Line with Terminal. TidBITS Publishing, Inc. ISBN9781933671550.
- ^'nsterm - AppKit Terminal.app', terminfo.src, retrieved June 7, 2013
| Wikimedia Commons has media related to Terminal (macOS). |